The Vice President of India, also known as the Deputy Head of State, serves as the second-in-command to the President of India in the Republic of India.
The vice presidency is the second-highest constitutional position, following the president, and holds the second rank in the order of precedence.
It is also the first in line to succeed the President. The vice president holds the position of ex officio chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
Article 66 of the Indian Constitution outlines the procedure for electing the vice president.
The vice president is elected through an indirect process by the members of an electoral college, which includes members from both Houses of Parliament.
The election does not involve members of state legislative assembly.
The voting is conducted by the Election Commission of India using the system of proportional representation with single transferable votes.
Voting is conducted using a confidential ballot. In addition to their role as vice president, they also serve as the chancellor of both Panjab University and Delhi University.
Jagdeep Dhankhar, a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party, currently holds the position of vice president.

He assumed the position of vice president after emerging victorious over Margaret Alva, the nominee from the Indian National Congress, in the 2022 Indian vice presidential election.
The Vice President of India holds a position of great dignity and responsibility, acting as the nation’s second-highest constitutional office.
Qualifications of Vice President
To be eligible for election as the Vice President of India, an individual must meet several criteria similar to those required for the presidency, with some distinctions tailored to the Vice President’s unique roles. The requirements include:
- Being a citizen of India.
- Being at least 35 years old.
- Not holding any office of profit under the government.
A key difference from the eligibility for the President lies in the parliamentary membership requirement.
While a presidential candidate needs to be eligible for membership in the Lok Sabha, a Vice Presidential candidate must qualify for election as a member of the Rajya Sabha.
This is because the Vice President serves as the ex officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
It’s important to note that when serving in one of these capacities—either as Chairman of the Rajya Sabha or as President of India—the Vice President cannot perform the duties of both roles simultaneously.
Election of Vice President


The vice president is elected using an indirect process.
This involves an electoral college made up of members from both Houses of Parliament (Lok Sabha & Rajya Sabha), who are elected or nominated.
The election follows a method of proportional representation using single transferable votes, and the voting is done secretly.
The process of electing the vice president differs slightly from that of electing the president.
Unlike the election of the president, the members of state legislatures do not participate in the electoral college.
However, the nominated members of the Rajya Sabha are part of the electoral college for the vice presidential election.
In order to nominate a candidate for the position of vice president, a minimum of 20 electors must sign as proposers and another 20 electors must sign as seconders.
Each candidate is required to submit a security deposit of ₹15,000 (US$190) to the Reserve Bank of India.
The Election Commission of India, an independent constitutional entity, is responsible for conducting elections.
The election must take place within 60 days after the tenure of the current vice president ends.
The appointment of a returning officer for the election is often done by rotation, with the secretary-general of either House of Parliament being chosen for this role.


The returning officer publicly announces the next election and invites candidates to submit their nominations.
In order to be eligible for election and to express their intention to run for office, an individual must be proposed by a minimum of twenty Members of Parliament and seconded by at least twenty other Members of Parliament.
The returning officer carefully examines the nomination papers, and thereafter includes the names of all qualified candidates on the ballot.
The election is conducted using a proportional representation system, where single transferable votes are used and the voting process is kept confidential.
When voters rate the candidates, they provide a numerical value of 1 to their top choice, 2 to their second choice, and so forth.
The minimum number of votes needed for a candidate to win the election is determined by dividing the total number of valid votes by two and then adding one to the quotient, without considering any remainder.
In the event that no candidate receives the necessary number of first-preference votes, the candidate with the lowest number of first-preference votes is eliminated and their second-preference votes are redistributed.
The process is iterated until a contender achieves the necessary number of votes. Members who have been nominated are also eligible to participate in the election.
Once the election has concluded and the votes have been tallied, the returning officer announces the outcome of the election to the electoral college.


Subsequently, the returning officer submits the outcome to the Government of India (specifically, the Ministry of Law and Justice) and the Election Commission of India.
The government then officially announces the name of the individual elected as vice president in the Official Gazette.
The vice president has the option to relinquish their position by formally submitting a letter of resignation to the president. The resignation takes effect immediately upon acceptance.
If the Vice President resigns, the vacant position must be filled promptly, however in the case of the President, an election must be conducted within a period of 6 months.
Term of the Vice President
The tenure of the vice president lasts for a duration of five years.
The vice president is eligible for unlimited re-election.
Nevertheless, the tenure of the office can be prematurely concluded due to mortality, voluntary departure, or dismissal.
The Constitution does not establish a specific process for filling the position of vice president in case of an unexpected vacancy, except through re-election.
In the case that the vice president is unable to discharge their duties as the chairman of the Rajya Sabha, the deputy chairman of the Rajya Sabha can assume these responsibilities.
Nevertheless, in the event of the president’s death while in office, the vice president assumes the role of president and can serve in that capacity for a maximum duration of 6 months, during which a new president must be elected.
Removal of the Vice President
According to the Constitution, the vice president can be dismissed by a resolution of the Rajya Sabha, which requires a majority of all the members at that time.
This resolution must also be agreed upon by the Lok Sabha, with a simple majority, as stated in Article 67(b).
However, it is not permissible to propose such a resolution unless a minimum of 14 days’ prior notice has been provided.
Significantly, the Constitution does not enumerate reasons for removal.
Article 122 of the constitution states that the chairman of the Rajya Sabha cannot be challenged in any court of law. Additionally, no vice president has ever been removed from office.
According to Article 71(1) of the constitution, the Supreme Court has the authority to remove the vice president from office if they engage in electoral malpractices or fail to meet the eligibility requirements for the Rajya Sabha.
According to Article 71(1), the Supreme Court is required to investigate any doubts regarding the behavior of a vice president and, if they are deemed to have shown disrespect for the Constitution, remove them from office.
Salary and Pension of the Vice President
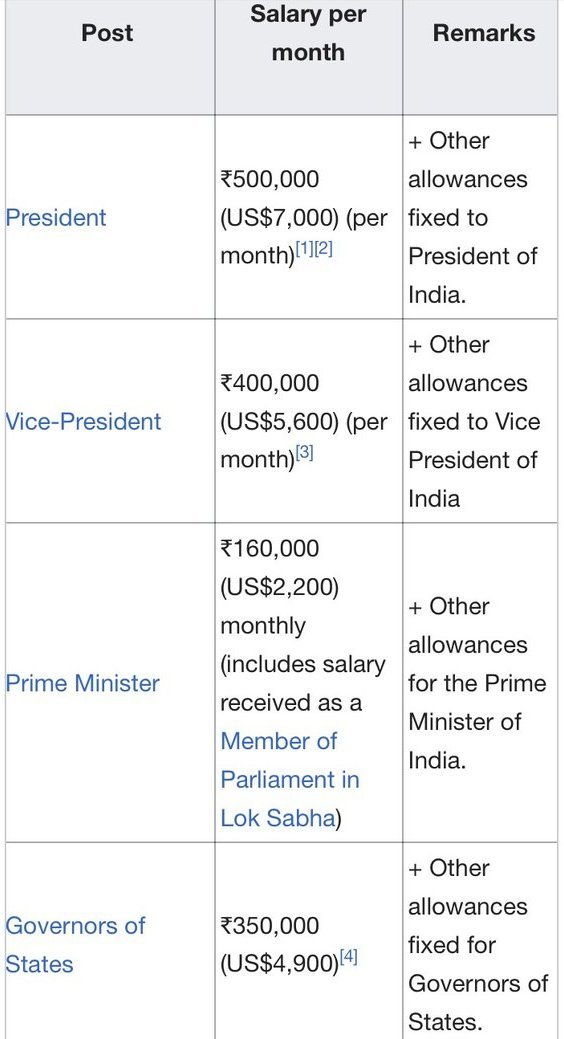

There is no provision for the remuneration of the Vice President of India in their official role.
The vice president is paid a salary for serving as the ex officio chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
Currently, the monthly compensation is ₹400,000 (US$5,000), which was revised from ₹125,000 in 2018.
Furthermore, the vice president is granted complimentary furnished housing, medical care, travel arrangements, and other amenities.
According to the constitution, when the vice president assumes the role of the president or fulfills the responsibilities of the president, they are allowed to receive the income and advantages that come with being the president.
The pension granted to the vice president amounts to half of their income.
Indeed, he is the sole official who does not get any remuneration or benefits associated with his specified position, namely the vice presidency.
Key powers and duties


While often perceived as a ceremonial role, the Vice President’s duties and powers are well-defined in the Indian Constitution and play a crucial role in the governance and legislative process of the country.
Here are the key powers and duties:
1. Chairperson of the Rajya Sabha:
- The primary role of the Vice President is to serve as the ex-officio Chairperson of the Rajya Sabha (the Upper House of Parliament).
- In this capacity, the Vice President is responsible for presiding over Rajya Sabha sessions, ensuring decorum, guiding debates, deciding on points of order, and interpreting the rules of the House.
2. Acting President:
- In the absence of the President due to resignation, removal, death, or inability to discharge their functions, the Vice President assumes the role of the Acting President of India until a new President is duly elected.
- The Vice President also acts as the President when the latter is unable to perform their duties due to absence, illness, or any other reason.
3. Ceremonial Duties:
- The Vice President represents India at official functions and ceremonial occasions, both within the country and abroad, in the absence of the President.
- They may also host visiting dignitaries and represent the country at international forums in the absence of the President.
4. Promotion of Education and Culture:
- While not explicitly mentioned in the Constitution, the Vice President often contributes to the promotion of education, culture, and other areas of national importance through their participation and leadership in various academic and cultural institutions.
5. Member of the Parliament’s Joint Sitting:
- When there is a deadlock between the two Houses of Parliament over a bill, the President can summon a joint sitting, which is presided over by the Vice President in their capacity as the Chairperson of the Rajya Sabha.
Powers in Specific Circumstances:
- The Vice President does not possess executive powers similar to the President but steps into the latter’s shoes under specific circumstances outlined by the Constitution.
- The powers while acting as President are nearly the same as those of the President, including making appointments, signing bills into law, and issuing pardons, albeit in a temporary capacity.
The Vice President’s role is pivotal in ensuring the stability and functionality of India’s constitutional and parliamentary processes, reflecting the importance of this dignified office in the democratic framework of the country.
References :
- https://vicepresidentofindia.nic.in/#:~:text=Vice%20President%20Of%20India%20Shri%20Jagdeep%20Dhankhar&text=The%20Vice%2DPresident%2C%20Shri%20Jagdeep,Uttarakhand%20on%20April%205%2C%202024.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vice_President_of_India
- https://www.india.gov.in/my-government/whos-who/vice-president
- https://byjus.com/free-ias-prep/vice-president/
- https://unacademy.com/content/ssc/study-material/indian-polity-and-constitution/the-vice-president/
- https://blogmedia.testbook.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/the-vice-president-of-india-know-about-roles-responsibilities-job-profile-salary-be75d6dd.pdf
- https://www.constitutionofindia.net/articles/article-67-term-of-office-of-vice-president/
- https://cms.rajyasabha.nic.in/careers_documents/1611147317407.09_Ex-officio-position.pdf
- https://www.indiacode.nic.in/show-data?actid=AC_CEN_22_29_00001_194938_1517807318353§ionId=141§ionno=12&orderno=15



